
科研进展
重庆研究院在多尺度水环境模型研究中取得系列进展
时间:2024-03-08编辑:智慧流域研究中心
在微观尺度上,针对污泥性质复杂多变使得其调理脱水过程难以量化控制的难题,研究了污泥多理化特性协同影响调理过程的规律,建立了量化调理剂添加量的多因子耦合模型,构建了一个“双系统”概念模型,用于表征污泥的调理与脱水过程,相关性系数从传统模型的0.54提升至新模型的0.93。相关研究成果以" Synergistic effect of organic matter-floc size-bound water and multifactorial quantitative model of optimal reagent demand in sewage sludge conditioning process prior to dewatering "为题发表于《Water Research》。

图1 污泥调理脱水“双系统”影响模型
在河库尺度上,针对水动力条件变化诱发水库泥沙沉积、水体富营养化、水华频发等大型河库系统亟待突破的难题,构建了三峡水库全库区干支流水动力-泥沙-水质耦合模型,揭示了潮汐式调度对三峡水库水动力条件、物质通量、物质滞留率的影响机制。相关研究成果以" Large-scale sediment and phosphorus transport in the Three Gorges Reservoir based on a new reservoir operation method. Environmental Research "为题发表于《Environmental Research》。
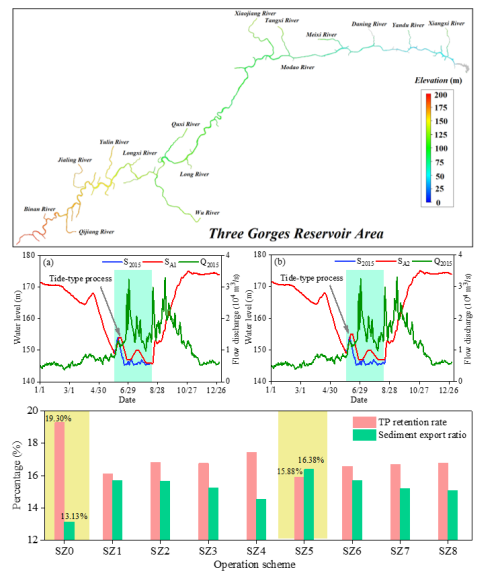
图2 基于水动力-泥沙-水质耦合模型的潮汐式调度下水沙和磷输移特征
在流域尺度上,针对大中型流域碎片化管理方式难以实现最佳治理效果的问题,在水环境模拟基础上引入了Gi* statistic算法,揭示了非点源污染在流域中的聚集特征,从流域管理的角度为辨识嘉陵江水污染的关键治理区提供了新的思路。相关研究成果以"Identifying critical regions for nitrogen and phosphorus loss management in a large-scale complex basin: The Jialing River"为题发表于《Environmental Research》。
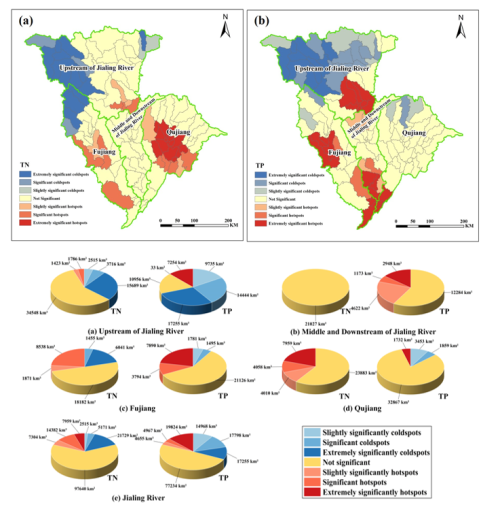
图3 基于水环境模型的嘉陵江关键治理区分布及面积特征
论文信息:
(1) Tan, X., Zeng, S.D., Chen, Z., Lv, M.Q., Tang, X.Y., He, X.X., Chen, Y.J., Wan, Y., Zhang, J.P., 2024. Synergistic effect of organic matter-floc size-bound water and multifactorial quantitative model of optimal reagent demand in sewage sludge conditioning process prior to dewatering. Water Research. 251, 121108. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2024.121108.
(2) Tang, X.Y., Zeng, S.D., Huang, G.X., Tong, S.C., Qiao, F., Ren, Y.X, Zhang, X.X., 2023. Large-scale sediment and phosphorus transport in the Three Gorges Reservoir based on a new reservoir operation method. Environmental Research. 233, 116386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2023.116386.
(3) Ren, Y., Xia, J., Zeng, S., Song, J., Tang, X., Yang, L., Lv, P., Fan, D., 2023. Identifying critical regions for nitrogen and phosphorus loss management in a large-scale complex basin: The Jialing River. Environmental Research. 232, 116359. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2023.116359.